Effective Carbon Footprint Calculation for Enterprises
How Businesses Can Measure, Manage, and Reduce Their Environmental Impact
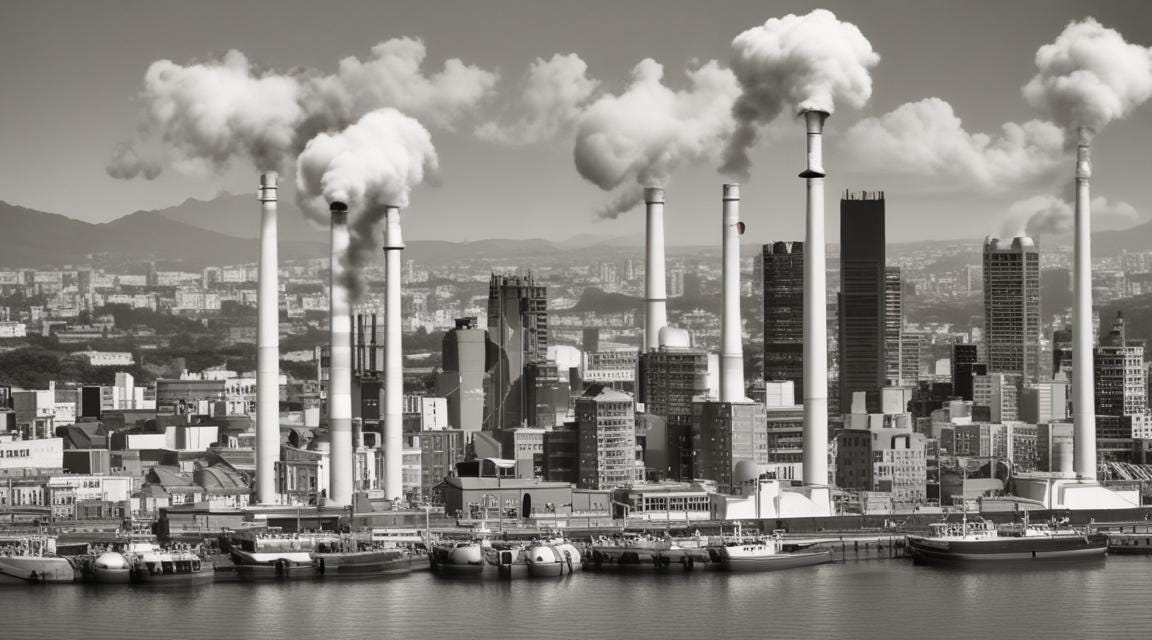
In today's world, the importance of sustainability and environmental responsibility is undeniable. Enterprises, regardless of their size or industry, play a crucial role in mitigating climate change. One of the most significant steps towards this goal is accurately calculating and managing the carbon footprint of an organization. This blog will delve into the effective methods of carbon footprint calculation for enterprises, highlighting key steps, tools, and benefits.
Understanding Carbon Footprint
A carbon footprint measures the total greenhouse gases (GHGs) emitted directly or indirectly by an enterprise, expressed in terms of carbon dioxide equivalents (CO2e). These emissions typically arise from various activities such as energy consumption, transportation, manufacturing processes, waste management, and even the supply chain.
Why Calculate Your Carbon Footprint?
Regulatory Compliance: Governments worldwide are implementing stricter regulations to curb GHG emissions. Calculating your carbon footprint ensures compliance with these regulations, avoiding potential fines and sanctions.
Environmental Impact: By understanding your emissions, you can implement strategies to reduce them, contributing to global efforts to combat climate change.
Cost Savings: Reducing energy consumption and optimizing processes can lead to significant cost savings.
Reputation: Demonstrating a commitment to sustainability can enhance your brand image and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers and investors.
Steps to Calculate Your Carbon Footprint
Define Boundaries:
Organizational Boundaries: Decide whether to include only your operations or extend to subsidiaries and joint ventures.
Operational Boundaries: Classify your emissions into three scopes:
Scope 1: Direct emissions from owned or controlled sources (e.g., company vehicles, onsite fuel combustion).
Scope 2: Indirect emissions from purchased electricity, steam, heating, and cooling.
Scope 3: Indirect emissions from your supply chain and other activities (e.g., business travel, waste disposal).
Collect Data:
Gather data on energy usage, fuel consumption, waste production, and other relevant activities. This may include utility bills, fuel receipts, and records of waste disposal.
Choose a Calculation Tool:
Utilize reliable tools and software to calculate your carbon footprint. Some popular options include:
GHG Protocol Calculator: Developed by the World Resources Institute, it offers comprehensive guidelines and tools.
EPA’s Simplified GHG Emissions Calculator: A user-friendly tool for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Carbon Trust’s Footprint Calculator: Suitable for a wide range of industries.
Convert Data to CO2e:
Use appropriate emission factors to convert your activity data into CO2e. Emission factors are coefficients that represent the emissions per unit of activity (e.g., kg CO2 per kWh of electricity).
Analyze and Report:
Compile your data and results into a comprehensive report. Highlight key sources of emissions and identify areas for improvement.
Set Reduction Targets:
Based on your findings, set realistic and measurable targets for reducing your carbon footprint. Develop a detailed action plan, outlining specific measures and timelines.
Tools and Resources
GHG Protocol: Provides standards, tools, and training for effective GHG accounting.
Carbon Trust: Offers resources and calculators for carbon footprinting and reduction strategies.
CDP (Carbon Disclosure Project): Encourages companies to disclose their environmental impact, providing a platform for benchmarking and improvement.
Benefits of Accurate Carbon Footprint Calculation
Enhanced Efficiency: Identifying high-emission areas can lead to more efficient processes and energy use.
Market Advantage: Many consumers and investors prefer companies with strong environmental credentials.
Risk Management: Reducing reliance on fossil fuels and improving sustainability can mitigate risks associated with energy price volatility and regulatory changes.
Innovation: Pursuing sustainability often drives innovation in products, services, and processes.
Conclusion
Calculating and managing your enterprise's carbon footprint is not only a regulatory necessity but also a strategic advantage. By understanding and reducing your emissions, you contribute to global sustainability efforts while reaping financial and reputational benefits. With the right tools and commitment, every enterprise can take meaningful steps towards a greener future.
Remember, the journey towards sustainability is continuous, and the impact of your efforts can be substantial. Start calculating your carbon footprint today and make a positive difference for tomorrow.